凭借长距离传输中的超低损耗,光纤已发展为光通信与光计算的关键平台。近年来,通过在纤上集成异质功能材料并增强光-物质相互作用,光纤器件在成像、传感与生物医学等领域得到广泛应用。相较于常规光纤,微纳光纤因其强倏逝场可显著提升光-物质耦合,展现出巨大的器件潜力;但其高曲率、小半径表面使异质材料的高质量共形集成长期受限。
近日,复旦大学智能机器人与先进制造创新学院/智慧纳米机器人与纳米系统国际研究院的梅永丰研究团队报道了一种面向微纳光纤的通用共形集成策略,可在光纤表面实现金属、氧化物、半导体与聚合物等多类纳米薄膜的紧密、全向包覆;并在此平台上演示了温度传感器、光学调制器、光栅与光电探测器等多种光纤器件,验证了其广泛适用性与功能可扩展性。相关成果《Conformal integration of multifunctional nanomembranes on fibers towards intelligent optical platform》以研究论文发表在Nature Communications上。
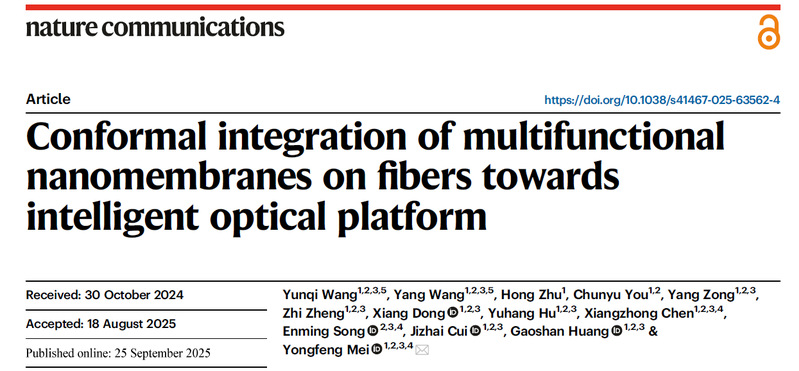
研究团队利用液体-薄膜界面能与薄膜弹性能为核心调控参量,通过预应变设计与液体辅助触发,使二维薄膜自发卷曲并转化为三维结构,并在光纤表面实现紧密、无缝、全向包覆。该方法具有较强的材料兼容性,可稳定在光纤上共形集成金属、氧化物、半导体与聚合物等多类纳米薄膜(见图1)。
图1:在微纳光纤表面实现多材料纳米薄膜共形集成的通用制造策略。
通过优化二维薄膜的平面图案设计、薄膜与光纤的相对位置控制,以及多层薄膜的组装顺序,研究团队实现了在不同光纤结构上对多材料三维微结构的阵列化、定制化共形集成(见图2)。在此基础上,进一步展示了集成多种功能材料的纤上器件与应用,包括温度传感器、气体传感器、光学调制器、光栅和光电探测器等,有效突破了传统光纤功能单一、异质材料难以集成的技术瓶颈。该工作推动光纤由单一光传输单元向高集成、多功能的光子平台演进,并为生物传感、光学计算、可穿戴与植入式器件等应用开辟新的技术路径。
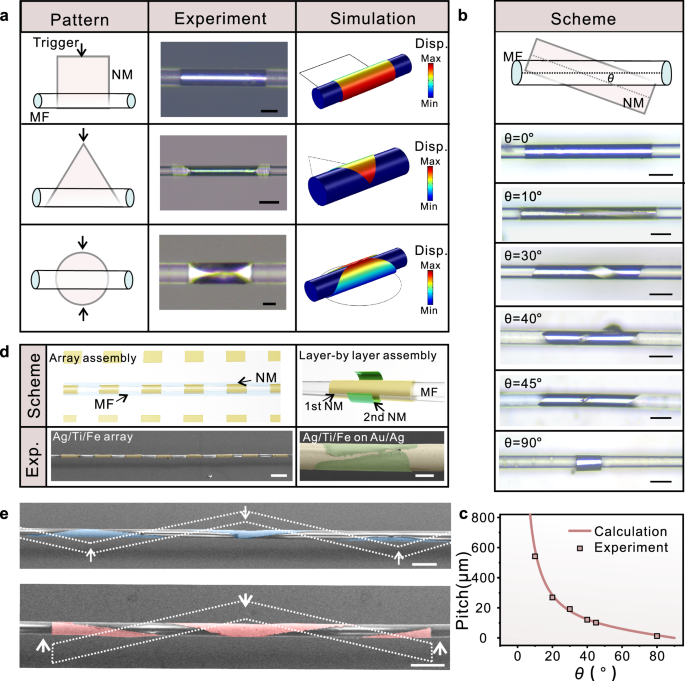
图2:基于精准组装实现多种三维微结构在微纳光纤上的共形集成。
复旦大学智慧纳米机器人与纳米系统国际研究院汪韫祺博士和汪洋博士为该论文共同第一作者,梅永丰教授为通讯作者。该工作得到了国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金、上海市科委等项目的资助和支持。
文章信息:
Yunqi Wang#, Yang Wang#, Hong Zhu, Chunyu You, Yang Zong, Zhi Zheng, Xiang Dong, Yuhang Hu, Xiangzhong Chen, Enming Song, Jizhai Cui, Gaoshan Huang & Yongfeng Mei*, Conformal integration of multifunctional nanomembranes on fibers towards intelligent optical platform, Nature Communications, 2025, 16, 8413.
原文链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63562-4
Conformal integration of multifunctional nanomembranes on fibers towards intelligent optical platform
Integrating materials onto optical fibers, enabling optical signal tuning during low-loss light transmission, is essential in optical communications, biosensors, and implantable devices. Such tuning, based on light-matter interaction, requires tight physical and optical contact between materials and fibers. However, large surface curvature (>105 m−1) of fiber makes it challenging for most materials to transfer onto fibers with tight contact, due to insufficient small-range forces. This induces weak light-matter interaction and ineffective optical coupling. Here, we propose a general strategy for conformal integration of nanomembranes—including metals, oxides, semiconductors, and polymers—onto microfibers. This integration relies on engineered elastic and surface energies between nanomembranes and fibers, enabling tight wrapping. We demonstrate homogeneous and inhomogeneous nanomembranes conformally integrated on microfibers, which are further developed into sensors, modulators, filters, and photodetectors as plug-and-play devices. Our study provides a versatile platform for integrating multifunctional materials on fibers, enabling health monitoring and on-fiber photonic computing.
Article information:
Yunqi Wang#, Yang Wang#, Hong Zhu, Chunyu You, Yang Zong, Zhi Zheng, Xiang Dong, Yuhang Hu, Xiangzhong Chen, Enming Song, Jizhai Cui, Gaoshan Huang & Yongfeng Mei*, Conformal integration of multifunctional nanomembranes on fibers towards intelligent optical platform, Nature Communications, 2025, 16, 8413.
Article link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63562-4
