有效地将光能、热能进行局域,从而达成高效的光-热-电能量转换,这一点对于实现更高性能的光热电探测至关重要。然而由于衬底的影响,目前微纳尺度下器件多物理场耦合作用机制的研究具有较大的挑战性。在片上集成器件向三维空间发展的趋势下,三维微纳器件的构效关系也需要详细探索。因此,利用纳米薄膜剥离组装技术将功能材料薄膜与衬底分离,构建独立的三维微纳结构,实现光、热能量局域,将为上述研究提供极大助力,为相应器件的实用化奠定重要基础。
近日,材料科学系黄高山/梅永丰课题组利用自卷曲技术,将作为光热电活性材料的碲纳米薄膜从衬底分离并组装成三维管状自驱动光探测器,揭示了器件中的光、热能量局域以及三维尺度下的光-热-电转换机制,实现了宽带光探测及灵敏度提升,为多维度光电探测提供了有效的解决方案。相关研究成果以“Enhanced photothermoelectric conversion in self-rolled tellurium photodetector with geometry-induced energy localization”为题,发表于Light: Science & Applications。

团队提出选用光热电活性材料,应用自卷曲纳米技术,利用纳米薄膜纵向内应变梯度,将从衬底释放的纳米薄膜组装成三维卷曲结构(图1a)。由于谐振效应,光场能量被局域在悬空的三维管壁中(图1b),产生更大的温度差,因此在热-电转换中产生了显著的电势差。实验结果进一步验证了管状探测器对光探测性能提升的显著效果,自驱动光生电压实现了307倍的提升。
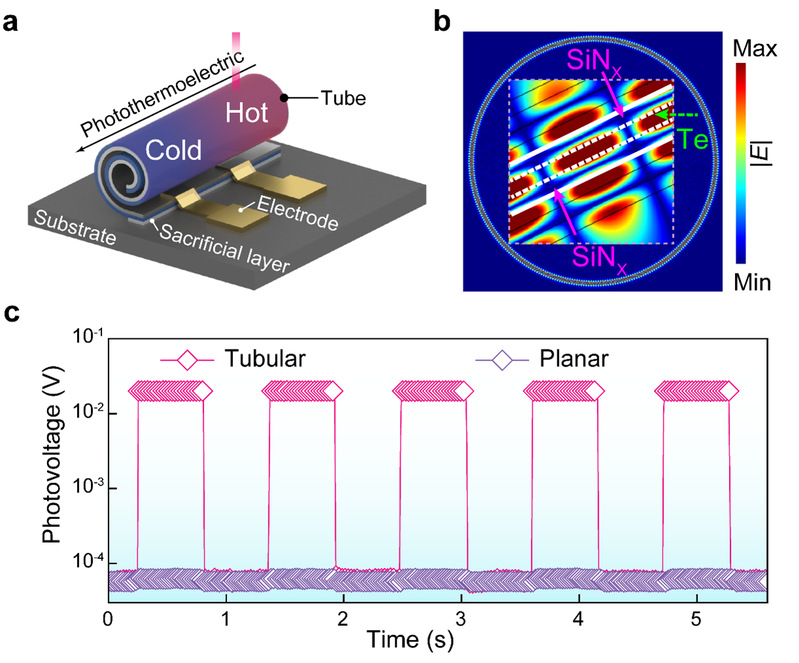
图1:自卷曲光热电探测器的结构及能量局域:a. 自卷曲光热电器件的结构和工作原理;b. 光激发下器件中的电场分布模拟结果;c. 相同激光脉冲照射下管状探测器和平面探测器的光生电压-时间关系曲线。
团队进一步验证了自卷曲探测器中的光热电效应及其位置依赖关系。图2a-b展示了自卷曲光热电器件中入射光位置与光生电流强度与方向的映射关系,验证了三维器件中光-热-电耦合与转换。本工作中所得到的自卷曲光热电探测器也被证实能够实现从可见光到长波红外超宽波段范围的自驱动光探测(图2c-d)。利用探测器卷曲圈数的调控,可以进一步优化自驱动光探测器的性能。
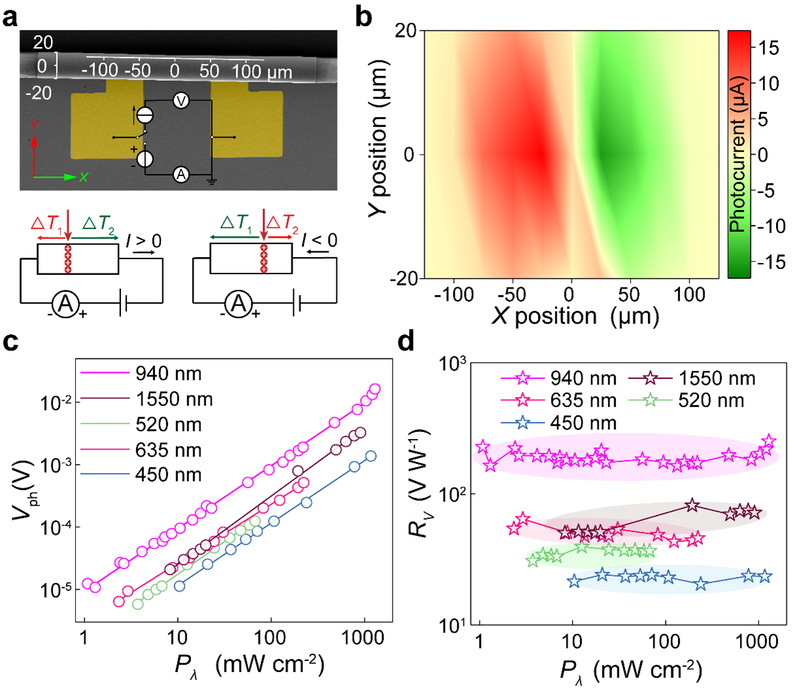
图2:自卷曲探测器的光热电效应验证:a-b. 研究所用空间坐标系,以及光生电流的位置依赖关系的示意图和实验结果;c-d. 多波长激发下入射光功率与自驱动光生电压,电压响应度关系曲线。
得益于管状探测器特殊的三维几何构型,自卷曲光热电探测器展现了优异的多维度信息探测能力。如图3a所示,自卷曲探测器展现了极佳的广角探测能力。此外,由于三维管状结构柱对称特性,探测器对电场方向平行于管轴方向的偏振光有更好的响应。自卷曲光热电探测器通过单像素传感实现了还原度极佳、分辨率极高的偏振成像,如图3b所示。该结果验证了自卷曲光热电探测器具备强度、偏振方向多维度探测能力。
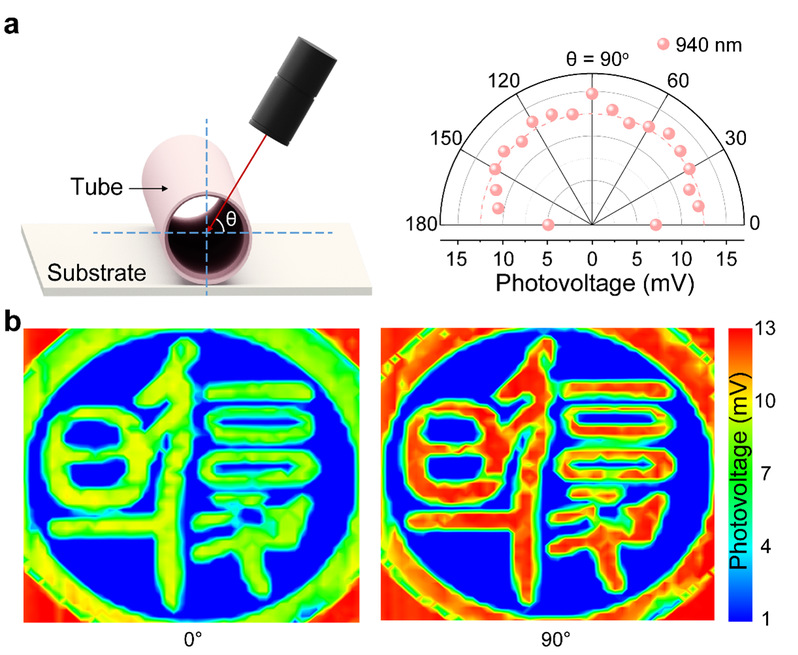
图3:自卷曲光热电探测器的全向探测与偏振成像:a. 卷曲探测器的广角探测能力示意图及角度分辨的光生电压测试结果;b. 在偏振入射角为0°和90°情况下自卷曲器件的成像结果。
本工作利用与现有成熟半导体技术兼容的三维自卷曲纳米技术结合热电功能材料,设计制备了新型自卷曲三维光热电探测器。三维管状结构有效地提高了光吸收和热局域作用,并利用光、热能量局域增强了光-热-电转化。本工作详细分析了三维尺度下的光-热-电多物理场耦合作用,并利用几何结构变化调控了探测器性能。该自卷曲光热电探测器具备高灵敏度、宽光谱响应范围等优异性能,还具备自驱动、全向探测、偏振成像等特色,在片上集成光电系统中具有广阔的应用前景。
复旦大学材料科学系硕士生黄嘉媛为论文的第一作者,黄高山教授为论文的通讯作者。该工作得到了国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金、上海市自然科学基金等经费支持。
文章信息:
Jiayuan Huang, Chunyu You, Binmin Wu, Yongfeng Mei, Gaoshan Huang* et. al., Enhanced photothermoelectric conversion in self-rolled tellurium photodetector with geometry-induced energy localization. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1), 153.
文章链接:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-024-01496-0
Enhanced photothermoelectric conversion in self-rolled tellurium photodetector with geometry-induced energy localization
Photodetection has attracted significant attention for information transmission. While the implementation relies primarily on the photonic detectors, they are predominantly constrained by the intrinsic bandgap of active materials. On the other hand, photothermoelectric (PTE) detectors have garnered substantial research interest for their promising capabilities in broadband detection, owing to the self-driven photovoltages induced by the temperature differences. To get higher performances, it is crucial to localize light and heat energies for efficient conversion. However, there is limited research on the energy conversion in PTE detectors at micro/nano scale. In this study, we have achieved a two-order-of-magnitude enhancement in photovoltage responsivity in the self-rolled tubular tellurium (Te) photodetector with PTE effect. Under illumination, the tubular device demonstrates a maximum photovoltage responsivity of 252.13 V W−1 and a large detectivity of 1.48 × 1011Jones. We disclose the mechanism of the PTE conversion in the tubular structure with the assistance of theoretical simulation. In addition, the device exhibits excellent performances in wide-angle and polarization-dependent detection. This work presents an approach to remarkably improve the performance of photodetector by concentrating light and corresponding heat generated, and the proposed self-rolled devices thus hold remarkable promises for next-generation on-chip photodetection.
Article information:
Jiayuan Huang, Chunyu You, Binmin Wu, Yongfeng Mei, Gaoshan Huang* et. al., Enhanced photothermoelectric conversion in self-rolled tellurium photodetector with geometry-induced energy localization. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1), 153.
Article link:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-024-01496-0
