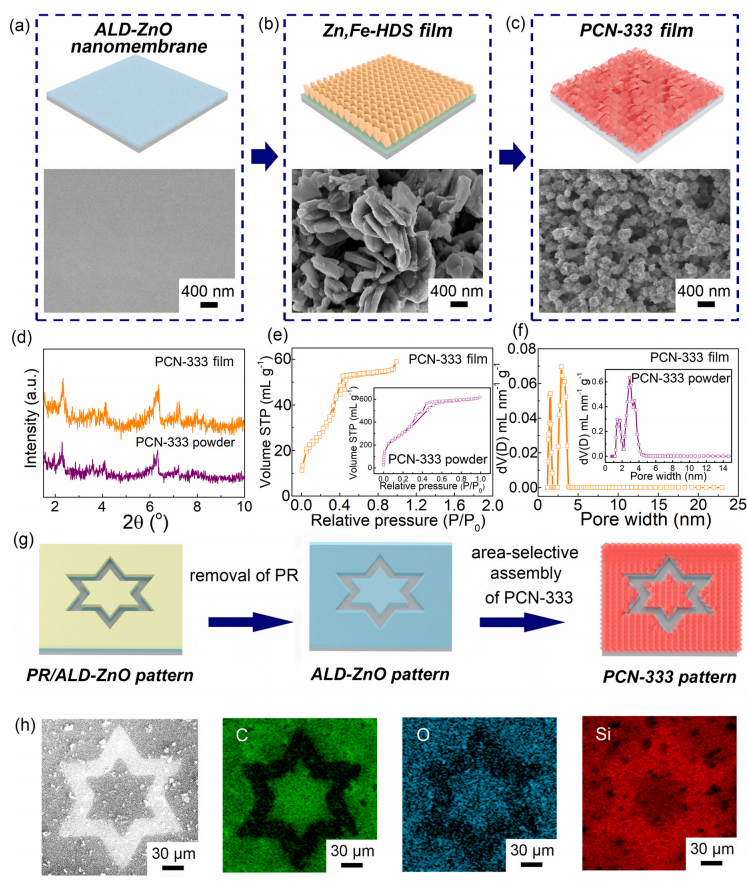
我院黄高山/梅永丰课题组在《今日纳米》(Nano Today)上发表题为《选域原子层沉积技术对MOF薄膜的精确自组装及其多巴胺传感应用》(“Area-selective and precise assembly of metal organic framework particles by atomic layer deposition induction and its application for ultra-sensitive dopamine sensor”)的研究工作。文章的第一作者为赵哲博士。文章报道了一种利用原子层沉积技术精准制备介孔铁基MOF薄膜的新策略,实现在平面和三维复杂衬底上的MOF薄膜的选域可控制备,并结合光刻等微纳加工技术,图形化定制MOF薄膜。作者选用三维衬底上保型性铁MOF薄膜作为多巴胺传感器,展示了高灵敏度传感性能。几十年来,纳米粒子的合成和开发一直吸引着研究人员。在纳米粒子中,金属有机物框架(MOF)粒子由于表面积大,结构可控,不饱和金属离子配位等特点收到了大量关注。为了基于 MOF活性材料制备器件,将MOF薄膜化并在衬底上集成成为了一个重要的方法。然而,MOF的薄膜化及精准控制仍然具有很大的挑战性。我院黄高山/梅永丰课题组利用原子层沉积技术沉积氧化物纳米薄膜作为诱导层,选域诱导制备介孔MOF薄膜。这种方法不仅可以实现MOF薄膜在平面衬底上的生长,也可以实现在三维复杂衬底上的MOF薄膜的制备。研究表明,该方法可以被拓展为一种MOF薄膜制备的普适性方法。
在三维框架上制备得到的铁基介孔MOF薄膜可应用于多巴胺电化学传感器的电极材料,实现4637.78 µA mM-1 cm-2的高灵敏度传感性能。该传感器同时具有较好的特异性和抗干扰能力。由于其结构稳定的特点,该传感器具备优异的循环性能和可重复性,在长达25小时的工作时间中性能不发生衰减,在多次测试中维持稳定的性能,标准差仅为4%。
我院提出了一种利用精准操纵、制备MOF薄膜的新策略,可以实现多种MOF在平面和三维复杂衬底上的普适性制备。基于MOF薄膜的复合结构具有良好的电化学性能,这为多功能集成的MOF芯片器件的制备提供了可能。
原文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1748013221002723?via%3Dihub
Prof. Gaoshan Huang / Prof. Yongfeng Mei 's research group from International Institute for Intelligent Nanorobots and Nanosystems published ‘Area-selective and precise assembly of metal organic framework particles by atomic layer deposition induction and its application for ultra-sensitive dopamine sensor’ in Nano Today. Dr. Zhe Zhao as the first author reported a new strategy for area-selective assembly of MOF particles to prepare a thin film with the assistance of atomic layer deposition (ALD)which realized the controllable preparation of MOF films on planar and three-dimensional complex substrates. The authors selected conformal MOF films on three-dimensional substrates as dopamine sensors, demonstrating high-sensitivity sensing performance. The synthesis and development of nanoparticles has fascinated researchers for decades. Among nanoparticles, metal-organic framework (MOF) particles have received a lot of attention due to their large surface area, controllable structure, and coordination of unsaturated metal ions. In order to fabricate devices based on MOF active materials, thin film formation and integration of MOFs on substrates has become an important method. However, weak interactions, non-uniformity and powdery assemblies limit the wide application of metal organic framework (MOF) in devices, the thinning and precise control of MOFs are still very challenging. Prof. Gaoshan Huang /Prof. Yongfeng Mei's research group from International Institute for Intelligent Nanorobots and Nanosystems used ALD technology to deposit oxide nano-films as inducing layers, and prepared mesoporous MOF films by domain selection. This method can not only realize the growth of MOF films on planar substrates, but also realize the preparation of MOF films on three-dimensional complex substrates. The study shows that this method can be extended as a universal method for MOF thin film preparation. In this work, self-assembled hierarchically porous Fe-based MOF (PCN-333) films were formed on both flat and complex three-dimensional (3D) substrates by combining gas and liquid fabrication approaches, and can be precisely patterned with photolithography. Researchers from our institute demonstrate that the PCN-333 film obtained possesses excellent electrochemical activity and can be applied in dopamine sensing for ultra-high sensitivity of 4637.78 µA mM−1 cm−2 with a wide linear range and a low limit of detection. The film has good specificity and anti-interference ability at the same time. Due to its stable structure, the PCN-333 film has excellent cycle performance and repeatability, with no degradation in performance for up to 25 hours of working time, and maintains stable performance in multiple tests with a standard deviation of only 4%. Moreover, the PCN-333 film composite achieves a function of good selectivity of distinguishing dopamine and ascorbic acid. This strategy is promising to prepare MOF film-based on-chip devices with advanced functions.
