金属有机框架(MOF)的固有孔径通常集中在微孔范围,小尺寸孔径会不可避免的限制分子的穿透,导致催化反应的反应物/产物的扩散受限,阻碍性能提升。保留MOF晶体原始微孔,并引入大孔是打破微孔限制,实现快速传质有效策略。然而此前文献中仅实现刚性颗粒态大孔-微孔MOF晶体的合成,而刚性晶体颗粒由于独立分布和团聚特性在催化反应中会导致电子传导网络不稳定和晶体团随机分布。

近日,我院黄高山/梅永丰团队与东华大学赵哲/刘宣勇团队合作在Advanced Functional Materials上发表了题为“Design and Assembly of Continuous Macro-Micro-Porous Metal-Organic Framework Film Assisted by Atomic Layer Deposition for Biosensing”的研究论文,文中提出了一种构建分级三维有序大孔-微孔结构MOF薄膜的策略,连续的大孔-微孔MOF薄膜中的质量扩散和电荷传输得到了显著改善,赋予了薄膜优异的催化活性。
该研究工作在三维有序的聚苯乙烯微球模板表面通过原子层沉积ZnO纳米膜作为诱导层,当饱和前驱体溶液填充到模板的空隙中时,MOF在ZnO纳米膜的诱导下逐步结晶,形成薄膜结构。用有机溶剂去除模板后,就形成了具有有序大孔-微孔的MOF薄膜。该策略不仅可以实现大孔孔径的按需调控,MOF的种类也多样可变。该研究将有序大孔-微孔ZIF-67薄膜与柔性器件集成,制备出的皮肤汗液葡萄糖传感器,具有高达5280 µA mM-1 cm-2的灵敏度和低至0.28 µM的检测限,传感性能远远高于大孔-微孔ZIF-67晶体和常规ZIF-67薄膜。性能提升主要归因于葡萄糖分子的快速扩散、相互连接的大孔通道增强活性位点的暴露以及稳定的电子传导网络。
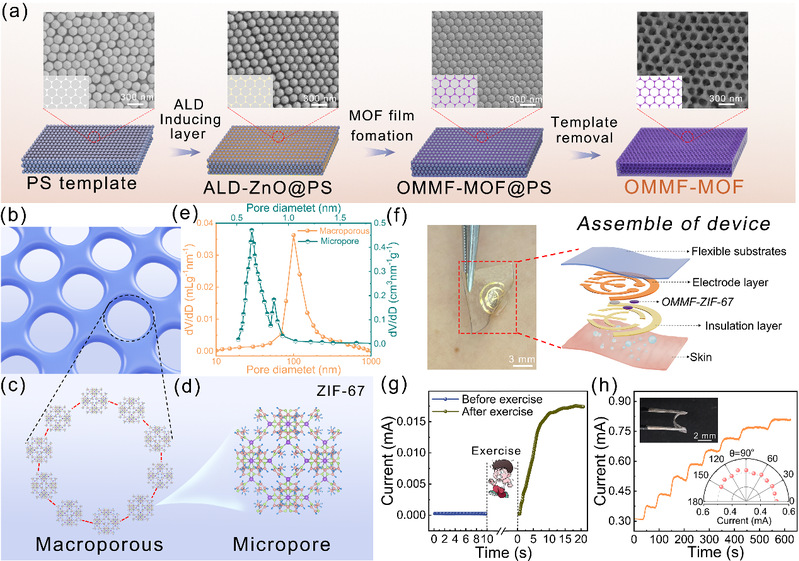
图1 有序大孔-微孔结构MOF薄膜的制备过程、形貌、结构模型、传感装置和性能。
复旦大学智慧纳米机器人与纳米系统国际研究院博士生王金龙为该论文的第一作者,黄高山教授和赵哲副教授为论文的通讯作者。该工作得到了国家重点技术研发计划、国家自然科学基金、上海市科学技术委员会、上海人才计划、中央高校基本科研业务费专项和纤维材料改性国家重点实验室的支持。
文章信息:
J. L. Wang, Y. Y. Jiang, F. Y. Zhu, Y. Mei, Z. Y. Qiao, Z. Zhao, Z. Zheng, Z. H. Lu, X. Y. Liu, Y. F. Mei, G. S. Huang, Design and Assembly of Continuous Macro-Micro-Porous Metal-Organic Framework Film Assisted by Atomic Layer Deposition for Biosensing, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2419775.
文章链接:
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202419775
Design and Assembly of Continuous Macro-Micro-Porous Metal-Organic Framework Film Assisted by Atomic Layer Deposition for Biosensing
Constructing highly oriented and ordered macro-pores on metal-organic framework (MOF) film can surpass the inherent limitations from micro-pores, promote multiphase adsorption, and expedite electrochemical reaction, but the fabrication remains extremely challenging. Here, continuous macro-micro-porous MOF films are achieved by combining polystyrene microsphere template and induction effect of ZnO nanomembrane prepared by atomic layer deposition. In addition to the intrinsic micro-pores, the fabricated MOF film exhibits oriented and ordered macro-porous structures. Compared with the macro-porous MOF particles and conventional MOF film, the mass diffusion and charge transportation in the macro-micro-porous MOF film are significantly improved, endowing the film with excellent electrochemical activity. The sensor device made from macro-micro-porous ZIF-67 film toward glucose exhibits excellent performance, e.g., high sensitivity, low limit of detection, and fast response, due to rapid glucose molecule diffusion and enhanced exposure of active sites via interconnected macro-porous channels. This work paves the way for the application of MOF film in high-performance biosensor chip and therefore may have great potential in post-Moore period.
Article information:
J. L. Wang, Y. Y. Jiang, F. Y. Zhu, Y. Mei, Z. Y. Qiao, Z. Zhao, Z. Zheng, Z. H. Lu, X. Y. Liu, Y. F. Mei, G. S. Huang, Design and Assembly of Continuous Macro-Micro-Porous Metal-Organic Framework Film Assisted by Atomic Layer Deposition for Biosensing, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2419775.
Article link:
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202419775
